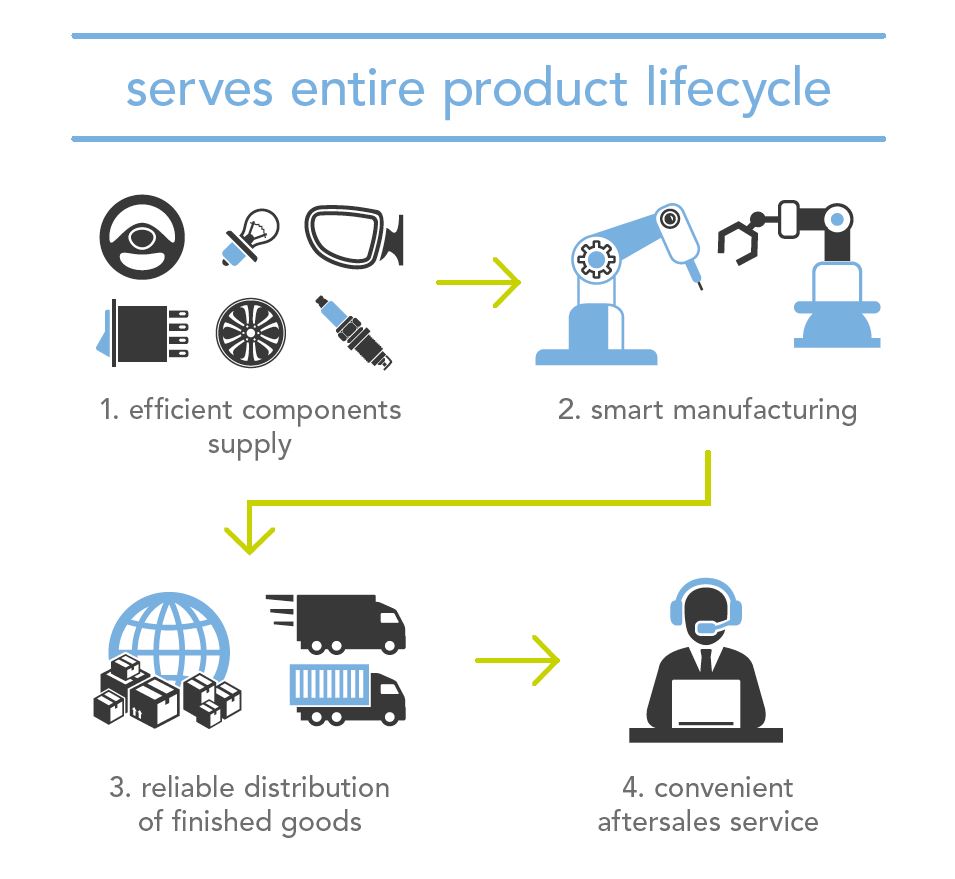
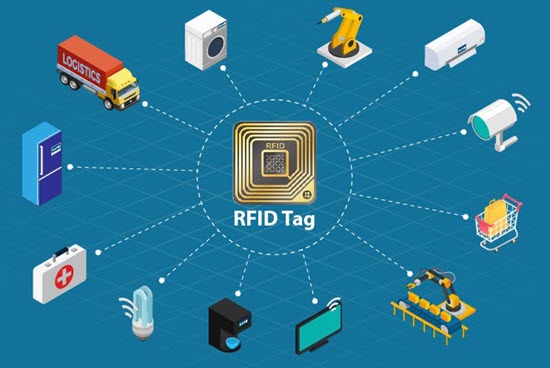
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is one of the fundamental pillars of Industry 4.0. It enables the identification, tracking, and management of objects and materials automatically and without contact. Thanks to RFID tags, it is possible to collect real-time data and monitor the entire product life cycle, from production to distribution, retail, and beyond.
RFID stands out for its ability to:
- Improve material traceability: Each component can be uniquely identified, allowing for continuous monitoring along the entire supply chain.
- Optimize inventory management: Real-time stock updates reduce errors and inefficiencies.
- Support automation in production processes: RFID systems integrated with other IoT technologies allow for more flexible and responsive production management.